13.15 The Q-value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by Q = [ mA + mb – mC – md]c2
where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
(i) \({ }_{1}^{1} \mathrm{H}+{ }_{1}^{3} \mathrm{H} \rightarrow{ }_{1}^{2} \mathrm{H}+{ }_{1}^{2} \mathrm{H}\)
(ii) \({ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C}+{ }_{6}^{12} \mathrm{C} \rightarrow{ }_{10}^{20} \mathrm{Ne}+{ }_{2}^{4} \mathrm{He} \)
Atomic masses are given to be
m (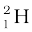 ) = 2.014102 u
) = 2.014102 u
m (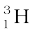 ) = 3.016049 u
) = 3.016049 u
m (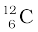 ) = 12.000000 u
) = 12.000000 u
m (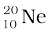 ) = 19.992439 u
) = 19.992439 u

© 2026 GoodEd Technologies Pvt. Ltd.