A bus starts from rest and moves with constant acceleration 8m/s-2. At the same time, a car travelling with a constant velocity 16 m/s overtakes and passes the bus. After how much time and at what distance, the bus overtakes the car?
1. t = 4 s, d = 64 m
2. t = 5 s, d = 72 m
3. t = 8 s, d = 58 m
4. None of the above




A lift is moving in upward direction. The total mass of the lift and the passengers is 1600 kg. The variation of the velocity of the lift is as shown in the figure. The tension in the rope at t = 8 s will be
1. 11200 N
2. 16000 N
3. 48000 N
4. 12000 N
Find the acceleration of light pulley is

1. F/m
2. F/2 m
3. F/4 m
4. F/8 m
Consider a planet in some solar system which has a mass double the mass of the Earth and a density equal to the average density of the Earth. An object weighing \(W\) on the Earth will weight:
1. \(W\)
2. \(2W\)
3. \(W/2\)
4. \([(2)^{1/3}]W\) at the planet
A boat is sent across a river a velocity of 8 . If the resultant velocity of the boat is 10 , the river is flowing with a velocity of
1. 12.8
2. 6
3. 8
4. 10
Two balls are thrown horizontally from the top of a tower with velocities and in opposite directions at the same time. After how much time, the angle between velocities of balls becomes 90º?
1.
2.
3.
4.
A box is placed on an inclined plane and has to be pushed down. The angle of inclination is
1. equal to the angle of friction
2. more than the angle of friction
3. equal to the angle of repose
4. less than the angle of repose
The escape velocity from the earth is about 11. The escape velocity from a planet having twice the radius and the same mean density as the earth is
1. 22
2. 11
3. 5.5
4. 15.5
A particle having a charge \(10~\text{mC}\) is held fixed on a horizontal surface. A block of mass \(80~\text{g}\) and having charge stays in equilibrium on the surface at a distance of \(3~\text{cm}\) from the first charge. The coefficient of friction between the surface and the block is \(\mu=0.5\). Find the range within which the charge on the block may lie:
| 1. | \(-4\times10^{-9}~\text{C}~\text{to}~4\times 10^{-9}~\text{C}\) |
| 2. | \(-2\times10^{-9}~\text{C}~\text{to}~2\times 10^{-9}~\text{C}\) |
| 3. | \(-4\times10^{-19}~\text{C}~\text{to}~4\times 10^{-19}~\text{C}\) |
| 4. | \(-2\times10^{-19}~\text{C}~\text{to}~2\times 10^{-19}~\text{C}\) |
In Young’s double-slit experiment, (slit distance d) monochromatic light of wavelength \(\lambda\) is used and the figure pattern observed at a distance L from the slits. The angular position of the bright fringes is:
\(1. \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{N \lambda}{d}\right)\)
\(2. \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{\left(N+\frac{1}{2}\right) \lambda}{d}\right)\)
\(3. \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{N \lambda}{L}\right)\)
\(4. \sin ^{-1}\left(\frac{\left(N+\frac{1}{2}\right) \lambda}{L}\right)\)
Two short magnets of equal dipole moments M are fastened perpendicularly at their centres as given in the figure. The magnitude of the magnetic filed at a distance d from the centre on the bisector of the right angle is
1.
2.
3.
4.
1. \(
{K}_{eq}{=}\frac{{L}_{1}{+}{L}_{2}}{\frac{{L}_{1}}{{K}_{1}}{+}\frac{{L}_{2}}{{K}_{2}}}\)
2. \(
{K}_{eq}{=}\frac{{L}_{1}{+}{L}_{2}}{{K}_{1}{K}_{2}}\)
3. \(
{K}_{eq}{=}\frac{{L}_{1}}{{K}_{1}{+}{K}_{2}}{+}\frac{{L}_{2}}{{K}_{1}{+}{K}_{2}}\)
4. \(
{K}_{eq}{=}\frac{{L}_{1}{L}_{2}}{{L}_{1}{+}{L}_{2}}\)
 and
and
| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
Three long wires, each carrying current i are placed parallel to each other. The distance between I and II is 3d, between II and III is 4 d and between III and I is 5d. Magnetic field at side of wire II is
1.
2.
3.
4.
In the following diagrams, a particle with small charge – q is free to move up or down, but not sideways near a larger fixed charge Q. The small charge is in equilibrium because in the positions shown, the electrical upward force is equal to the weight of the particle. Which statement is true?
1. In figure a, -q is in stable equilibrium.
2. In figure a, -q is in neutral equilibrium.
3. In figure b, -q is in stable equilibrium.
4. Neither in fig(a) nor in fig(b) , q is in stable equilibrium.

Assume that the nuclear binding energy per nuclear \((B/A)\) versus mass number \((A)\) is as shown in the figure. Use this plot to choose the correct choice(s) given below:
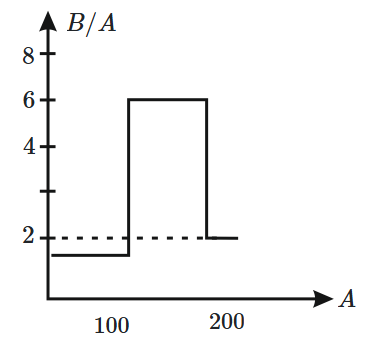
1. Fusion of two nuclei with mass number lying in the range of \(51<A<100\) will release energy
2. Fission of a nucleus lying in the mass range of \(200<A<260\) will release energy when broken into two equal fragments
3. Both \(1\) and \(2\)
4. None of these
Three identical capacitors A, B and C are charged to the same potential and then made to discharge through three resistance . Their potential differences (V) are plotted against time t, giving the curves 1, 2 and 3. Choose the incorrect option.
1.
2.
3.
4. None of the above.
| 1. | wide, and is flanked by alternate dark and bright bands of decreasing intensity |
| 2. | narrow, and is flanked by alternate dark and bright bands of equal intensity |
| 3. | wide, and is flanked by alternate dark and bright bands of equal intensity |
| 4. | narrow and is flanked by alternate dark and bright bands of decreasing intensity |
The logic circuit as shown below has the input waveforms A and B as shown. Pick out the correct output waveform. 

1.
2.
3.
4.
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) Linear momentum of a body changes even when it is moving uniformly in a circle.
Reason (R) In uniform circular motion velocity remains constant.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
3. Assertion is true but reason is false.
4. Both assertion and reason are false.
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) Conductors having equal positive charge and volume, must also have same potential.
Reason (R) Potential depends only on charge and volume of conductor.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | The positively charged nucleus of an atom has a radius of almost \(10^{-15}~\text{m}\). |
| Reason (R): | In \(\alpha\text-\)particles scattering experiment, the distance of closest approach for \(\alpha\text-\)particles is \(\approx 10^{-15} ~\text{m}\) |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) The phenomenon of X-ray production is basically inverse of the photoelectric effect.
Reason (R) X-rays are electromagnetic waves.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) When capacitive reactance is smaller than the inductive reactance in L-C-R circuit, emf leads the current.
Reason (R) The phase angle is the angle between the alternation emf and alternation current of the circuit.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) A brass tumbler feels much colder than a wooden tray on a chilly day.
Reason (R) The thermal conductivity of brass is less than that of wood.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Given below are two statements:
| Assertion (A): | Electrons in the atom are held due to coulomb forces. |
| Reason (R): | This force is due to the induced charge on the conducting surface which is at zero potential. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | (A) is False but (R) is True. |
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) If a point charge q is placed in front of an infinite grounded conducting plane surface, the point charge will experience a force.
Reason (R) This force is due to the induced charge on the conducting surface which is at zero potential.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) If a proton and an α-particle enter a uniform magnetic field perpendicularly with the same speed, then the time period of revolution of the α-particle is double than that of proton.
Reason (R) In a magnetic field, the time period of revolution of a charged particle is directly proportional to mass.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) Critical angle of light passing from glass to air is minimum for violet colour.
Reason (R) The wavelength of violet light is greater than the light of other colurs.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) Electric conduction in gasses is possible at normal pressure.
Reason (R) The electric conduction in gases depends only upon the potential difference between the electrodes.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) The coil is bound over the metallic frame in moving coil galvanometer.
Reason (R) The metallic frame helps in making steady deflection without any oscillation.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) The focal length of lens does not change, when red light is replaced by blue light.
Reason (R) The focal length of lens does not depends on colour of light used.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) When two coils are wound on each other, the mutual induction between the coils is maximum.
Reason (R) Mutual induction does not depend on the orientation of the coils
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false
Direction: In each of the following questions, a Statement of assertion is given followed by a corresponding Statement of reason.
Assertion (A) Hydrogen atom consists of only one electron but its emission spectrum has many lines.
Reason (R) Only Lyman series is found in the absorption spectrum of hydrogen atom whereas in the emission spectrum, all the series are found.
1. Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
2. Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
3. Assertion is true but reason is false
4. Both assertion and reason are false

The mass of potassium dichromate crystals required to oxidize 750 of 0.6 M Mohr’s salt solution is (Given, molar mass, potassium dichromate = 294, Mohr’s salt = 392)
1. 0.39 g
2. 0.37 g
3. 22.05 g
4. 2.2 g
A quantity of hydrogen gas occupies a volume of 30.0 mL at a certain temperature and pressure. What volume would half this mass of hydrogen occupy at triple the absolute temperature if the pressure were one ninth that of the original gas?
1. 270 mL
2. 90 mL
3. 405 mL
4. 137 mL
Choose the incorrect statement among the following.
1. The chemistry of different lanthanoids is very similar
2. 4f and 5f-orbitals are equally shielded
3. D-block element show irregular and erratic chemical properties among themselves
4. La and Lu have partially filled d-orbitals and no other partially filled orbitals.
The Zone refining process of metals is based on the principle of
1. excess noble character of the liquid metal than that of impurity
2. lower melting point of the impurity than that of pure metal
3. greater solubility of impure metal than that of impurity
4. greater solubility of the impurities in the molten state than in the solid
Mixture X = 0.02 mole of [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br and 0.02 mole of [Co(NH3)5Br]SO4 was prepared in 2 L of solution.
In a gas lighter, mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy by using crystals of barium titanate. Barium titanate is
1. piezoelectric but not ferroelectric
2. both piezoelectric as well as ferroelectric
3. ferroelectric
4. neither ferroelectric nor piezoelectric


1. P-0, Q-1, R-2, S-3
2. P-3, Q-2, R-1, S-0
3. P-1, Q-2, R-3, S-0
4. P-0, Q-3, R-2, S-1
1. Van der Vaals’ forces
2. Hydrogen bond formation
3. Covalent attraction
4. lonic interaction
1. Calcium hydride and calcium carbide
2. Calcium carbide and aluminium nitride
3. Magnesium nitride and calcium nitride
4. Calcium phosphide and calcium cyanamide
The electrons identified by quantum numbers n and l
1) n = 4, l = 1
2) n = 4, l = 0
3) n = 3, l = 2
4) n = 3, l =1
can be placed in the order of increasing energy as
1.
2.
3.
4.





| I. |  |
| II. | CH3CH2NH2 |
| III. | (CH3)2NH |
| IV. | CH3CONH2 |
1. Kevlar
2. PHBV
3. Glyptal
4. Bakelite
1. α-4, β-3
2. α-2, β-3
3. α-5, β-3
4. α-7, β-4
1. radiation that only interacts with ions
2. the same as a proton
3. a neutron that has acquired a charge, thus forming an ion
4. high energy radiation that removes electrons from atoms or molecules
1. 8.2
2. 3.2
3. 9.3
4. 3.9
1. -12.64 kcal
2. -11.98 kcal
3. -13.68 kcal
4. -12.68 kcal
| 1. | –157.33 kJ | 2. | +201.033 kJ |
| 3. | –257.033 kJ | 4. | +257.033 kJ |
1. 55.28%
2. 37.3%
3. 45.00%
4. 49.01%
1. 1.98 atm
2. 2.09 atm
3. 2.36 atm
4. 1.48 atm
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) At the end of electrolysis using platinum electrodes, an aqueous solution of turns colourless.
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
| Assertion (A): | Adding inert gas to the dissociation equilibrium of N2O4 at constant temperature and pressure increases the dissociation. |
| Reason (R): | Due to the addition of inert gas molar concentration of reactants and products decreases. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) Generally alkali and alkaline earth metals form superoxides.
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
| Assertion (A): | pH value of the HCl solution is less than that of acetic acid of the same concentration. |
| Reason (R): | In equimolar solutions, the number of titratable protons present in HCl is less than that present in acetic acid. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) Nitration of salicyclic acid gives picric acid by elimination of group
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) Sulphanilic acid migrates to anode in basic medium and to cathode in acid medium.
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) Proteins, starch and rubber are lyophilic colloids.
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
| Assertion (A): | The order of stability of carbanion is (C6H5)3C- > C6H5CH2- > CH3- > (CH3)2CH- . |
| Reason (R): | The stability of carbanions is influenced by both resonance and inductive effects. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A) |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) Cs and undergo a violent reaction to form ionic compound CsF.
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
Assertion (A) Acyl halide are more reactive than acid substance amide toward nucleophilic substitution.
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
Consider the statements given below:
| Assertion (A): | The enthalpy of both graphite and diamond is taken to be zero, being elementary substances. |
| Reason (R): | For elementary substances in their standard state, the enthalpy of formation is taken as zero. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true, and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true, but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true, but (R) is false. |
| 4. | (A) is false, but (R) is true. |
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
In the following questions, a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
| Assertion (A): | Benzaldehyde is more reactive than ethanol toward nucleophilic attack. |
| Reason (R): | The overall effect of –I and + R effect of the phenyl group decreases the electron density on the the carbon atom of a  group in benzaldehyde. group in benzaldehyde. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are true but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is true but (R) is false. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are false. |
| Assertion (A): | The freezing point of 0.05 M urea solution is different from that of 0.05 M sodium chloride solution. |
| Reason (R): | The depression in the freezing point is directly proportional to the number of species present in the solution. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
Direction:In the following questions a statement of Assertion (A) followed by a statement of Reason (R) is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choice.
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
| Assertion (A): | [Ti(H2O)6]3+ is coloured, while [Sc(H2O)6]3+ is colourless. |
| Reason (R): | d-d transition is not possible in [Sc(H2O)6]3+ because no d-electron is present, while it is possible for Ti3+ as it has a d1 system. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true bu Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
| Assertion (A): | After splitting of d-orbitals during complex formation, the orbitals form two sets of orbitals \(t_{2g}\)and \(e_{g}\)octahedral field. |
| Reason (R): | Splitting of d-orbitals occurs only in the case of strong-field ligands such as CN-. |
| 1. | Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A). |
| 2. | Both (A) and (R) are True but (R) is not the correct explanation of (A). |
| 3. | (A) is True but (R) is False. |
| 4. | Both (A) and (R) are False. |
1. geographic barrier
2. barrier to gene flow
3. change in chromosome number
4. barrier to mating
Read the following statements regarding archaebacteria and Choose the incorrect statement.
I. Their cell wall lacks peptidoglycan.
II. They contain membrane-bound organelles.
III. These have distinct ribosomal RNA sequence.
IV. Lipid in the cell membrane of archaebacteria has a different structure than those in all other organisms.
1. I and II
2. Only II
3. Only IV
4. III and IV
1. Vertebrata
2. Urochordata
3. Invertebrates
4. Chordates
1. diphyodont, heterodont and thecodont
2. diphyodont, thecodont and heterodont
3. thecodont, diphyodont and heterodont
4. thecodont, heterodont and diphyodont
1. Gametophytic phase is dominant in life cycle
2. Fertilization takes place in presence of water.
3. Zygote undergoes meiosis to produce sporophyte.
4. Sporophyte is physiologically dependent on gametophyte
A bacterium divides every 35 minutes. If a culture containing 105 cells/mL is grown for 175 minutes, what will be the cell concentration/mL after 175 minutes?
1.
2.
3.
4.
1. use of habit and habitat of organisms
2. based on the presence or absence of chemicals in cells or tissues
3. based on morphological traits
4. based on evolutionary history of a species.

1. A – Fusiform, radish; B – Napiform, turmeric; C – Tuberous, sweet potato
2. A – Conical, turnip; B – Nodulated, sweet potato; C – Tuberous, Curcuma amada
3. A – Conical, carrot; B – Tuberous, sweet potato; C – Fasciculated, Dahlia
4. A – Napiform, carrot; B – Nodulated, Tamarind; C – Tuberous, turmeric
1. Clamp connections
2. Somatogamay between two hyphae of different strains
3. Both (a) and (b) are correct
4. Basidiospores
1. less amount of cytokinins in lateral buds
2. more amount of cytokinins in lateral buds
3. less amount of auxin in lateral buds.
4. more amount of auxin in lateral buds

1. A-5 B-3 C-4 D-1 E-2
2. A-5 B-2 C-1 D-4 E-3
3. A-2 B-5 C-4 D-1 E-2
4. A-5 B-3 C-4 D-2 E-1
1. Segregation – Metaphase II
2. Significance of meiosis – Production or genetically similar cells
3. Exchange of genetic material – Diakinesis
4. Anaphase II of meiosis – Centromeric division.
1. IX, X, XI and XII
2. III, VII and IX
3. VII, VIII, IX and X
4. VIII, IX, X, XI and XII
1. More than non – electrolyte
2. Less than non – electrolyte
3. Same as non – electrolyte
4. None of these
1. Vitamin-A - Fat soluble – Night blindness
2. Vitamin-K – Fat soluble – beri – beri
3. Vitamin-A – Fat soluble – beri – beri
4. Vitamin-K – Water soluble – Pellagra
1. 12
2. 8
3. 2
4. 3
1. Myopia - Biconvex lens
2. Olfactory - Smell
3. Algerireceptor - Pain
4. Organ of corti cells - Sensory and Supporting
1. Bacillus subtilis
2. Bacillus megatherium
3. Streptococcus lactis
4. Acetobacter aceti
1. Spike, corymb, hypanthodium
2. Spike, female catkin, hypanthodium
3. Unbel, catkin, spadix
4. Female catkin, corymb, spike
1. 4 n
2. 6 n
3. 2 n
4. 8 n

1. Exponential growth curve
2. Logistic growth curve
3. Both the growth curves
4. None of the above
1. ovule and microsporangia are present in same sporophyll
2. micro and megasporophyllus are present in same cone
3. male cone and megasporophylls are borne on the same plant
4. male cone and megasporophylls are borne on separate individual plants.
1. Progesterone
2. Luteinizing hormone
3. FSH
4. Human chorionic gonadotropic hormone
1. auxin and no cytokinin
2. higher concentration of auxin and lower concentration of cytokinin
3. Higher concentration of cytokinin and lower concentration of auxin
4. Both auxin and cytokinin in equal amounts
1. Blood glucose level increases by hydrolyzing glycogen in liver
2. Decreases blood sugar level by forming glycogen
3. Increase blood glucose level by stimulating glucagon production
4. Increases blood glucose level by promoting cellular uptake of glucose
1. euchromatin
2. heterochromatin
3. Both (a) and (b)
4. Neither euchromatin nor heterochromatin
1. are the reaction centres of PS-I and PS-II respectively
2. Light energy provides energy for the photolysis of water through excitation of the reaction centre of PS-II
3. NADPH is not produced in cyclic electrons transport in light reactions
4. Reactions of the two photosystems are needed for the reduction of NADP
1. Oncosphere, hexacanth, cysticercus, matured, proglottid, gravid
2. Matured proglottid, cysticercus, gravid, onchosphere, hexacauth
3. Hexacanth, cysticercus, gravid, onchosphere mature proglottid
4. Gravid, onchosphere, cysticercus, hexacanth, mature proglottid
1. Thyroid Gland - Secretin
2. Alpha cells of Pancreas - Glucagon
3. Adrenal Medulla of adrenal Gland - Thyroid
4. Intestinal Mucosa of duodenum and jejunum - Epinephrine

1. Sacrum, ilium, pubis, femur, tibia and fibula
2. ilium, pubis, sacrum, femur, fibula and tibia
3. Sacrum, pubis, ilium, femur, tibia and fibula
4. ilium, sacrum, pubis, femur, tibia and fibula
1. Collecting tube
2. Henle’s loop
3. Distal convoluted tubule
4. Proximal convoluted tubule
1. 230 mL
2. 210 mL
3. 190 mL
4. 150 mL
1. outgrowth of vessels of xylem
2. ingrowth of vessels
3. ingrowth of xylem parenchyma
4. swelling of xylem fibres for no function
1. Mouthparts of cockroach and butterfly
2. Wings of butterfly and bird
3. Wings of mosquito and butterfly
4. Forelegs of horse and paddies of whale
1. Cowper’s glands
2. prostate gland
3. seminal vesicles
4. epididymis
1. magnesium
2. copper
3. iron
4. manganese
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
2. Both Assertion and Reason are true, but Reason is not the correct explanation of Assertion
3. Assertion is true, but Reason is false
4. Both Assertion and Reason are false
1. Cowper’s glands
2. prostate gland
3. seminal vesicles
4. epididymis