A string with constant tension T is deflected through an angle by a smooth fixed pulley. The force on the pulley is
Traffic is moving at 60 km/hr along a circular track of radius 0.2 km, the correct angle of banking is
1.
2.
3.
4.
A massless, frictionless rope is attached at point \(A\) on the wall, then passes under a movable pulley \(P_2,\) goes up and over a fixed ceiling pulley \(P_1,\) and supports a hanging weight \(W_1.\) The movable pulley \(P_2\) carries a second weight \(W_2\) hanging directly beneath it. If \(W_1=W_2,\) what is the angle \((AP_2P_1)\) between the two rope segments meeting at \(P_2\text{?}\)
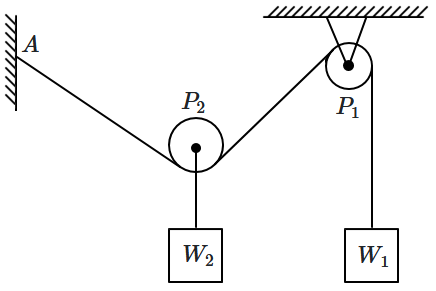
1. \(30^\circ\)
2. \(60^\circ\)
3. \(150^\circ\)
4. \(120^\circ\)
A light spring is compressed and placed horizontally between a vertical fixed wall and a toy car which is free to slide over a smooth horizontal table. If the system is released from rest, which graph best represents acceleration \(a\) and distance \(x\) covered by the car?

| 1. |  |
2. |  |
| 3. |  |
4. |  |
A rigid ball of mass \(M\) strikes a rigid wall at \(60^{\circ}\) and gets reflected without loss of speed, as shown in the figure. The value of the impulse imparted by the wall on the ball will be:
| 1. | \(Mv\) | 2. | \(2Mv\) |
| 3. | \(\dfrac{Mv}{2}\) | 4. | \(\dfrac{Mv}{3}\) |
Which one of the following statements is incorrect?
| 1. | Rolling friction is smaller than sliding friction. |
| 2. | The limiting value of static friction is directly proportional to the normal reaction. |
| 3. | Frictional force opposes the relative motion. |
| 4. | The coefficient of sliding friction has dimensions of length. |
A block of mass \(m\) is placed on a smooth inclined wedge \(ABC\) of inclination \(\theta\) as shown in the figure. The wedge is given an acceleration '\(a\)' towards the right. The relation between \(a\) and \(\theta\) for the block to remain stationary on the wedge is:
| 1. | \(a = \dfrac{g}{\mathrm{cosec }~ \theta}\) | 2. | \(a = \dfrac{g}{\sin\theta}\) |
| 3. | \(a = g\cos\theta\) | 4. | \(a = g\tan\theta\) |
A car is negotiating a curved road of radius \(R\). The road is banked at an angle \(\theta\). The coefficient of friction between the tyre of the car and the road is \(\mu_s\). The maximum safe velocity on this road is:
| 1. | \(\sqrt{\operatorname{gR}\left(\dfrac{\mu_{\mathrm{s}}+\tan \theta}{1-\mu_{\mathrm{s}} \tan \theta}\right)}\) | 2. | \(\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{g}}{\mathrm{R}}\left(\dfrac{\mu_{\mathrm{s}}+\tan \theta}{1-\mu_{\mathrm{s}} \tan \theta}\right)}\) |
| 3. | \(\sqrt{\frac{\mathrm{g}}{\mathrm{R}^2}\left(\dfrac{\mu_{\mathrm{s}}+\tan \theta}{1-\mu_{\operatorname{s}} \tan \theta}\right)}\) | 4. | \(\sqrt{\mathrm{gR}^2\left(\dfrac{\mu_{\mathrm{s}}+\tan \theta}{1-\mu_{\mathrm{s}} \tan \theta}\right)}\) |
Three blocks \(\mathrm{A}\), \(\mathrm{B}\), and \(\mathrm{C}\) of masses \(4~\text{kg}\), \(2~\text{kg}\), and \(1~\text{kg}\) respectively, are in contact on a frictionless surface, as shown. If a force of \(14~\text{N}\) is applied to the \(4~\text{kg}\) block, then the contact force between \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) is:
1. \(2~\text{N}\)
2. \(6~\text{N}\)
3. \(8~\text{N}\)
4. \(18~\text{N}\)










